- drranajitk@gmail.com
- 0 Comments
Often known to be as the “Silent Killer”, Ovarian Cancer is one of the significant gynecological cancers and poses a serious threat to women as it is often diagnosed at an advanced stage due to indefinite, unclear or ambiguous symptoms. Understanding its risk factors, knowing the potential symptoms and early detection methods can highly improve outcomes.
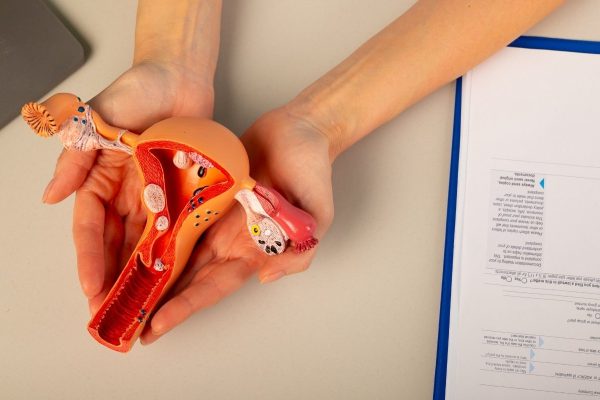
One of the most serious gynecological cancers, Ovarian Cancer can be often mistaken for simple digestive issues. Some of its warning whispers or signs may include;
- Continuous bloating or abdominal swelling
- Pelvic pain
- Abdominal pain
- Feeling full quicker or difficulty eating
- Frequent or urgent urination
- Constipation or other changes in bowel habits
- Fatigue & weight loss
With these symptoms being persistent and lasting for over a couple of weeks, one should see her doctor/oncologist immediately.
Identifying vulnerabilities or understanding its risk factors can be life saving. Certain factors responsible, that can increase the risk of developing ovarian cancer in women includes:
- Risk of ovarian cancer increases with age, mostly after menopause
- A strong family history of any gynaec or breast cancer
- Inherited genetic mutations in BRCA1 & BRCA2 genes pose a significant threat.
- Early menstruation and late menopause with never having given birth also poses a threat.
- Endometriosis
- Obesity
As said by oncologists and specialists globally, “Early detection is the key to survival”.
Though early detection is important in better survival rates, sadly, there is no dependable screening test for ovarian cancer in women without symptoms. But, certain knowledge or having awareness of the symptoms and taking a few steps regularly can help in early detection.
- Though not definitive, regular pelvic exams can identify abnormalities.
- CA-125 blood test
- Transvaginal Ultrasound
Combating Ovarian Cancer or treatment typically involves:
- Surgery, to remove ovaries, fallopian tubes, & potentially other affected parts or tissues.
- Chemotherapy can be used to kill cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy can be used to treat smaller areas of recurrent cancer
- Targeted Therapy
- Hormonal therapy in some cases
Note: By staying informed and updated of the risks, symptoms and treatment options, women can empower themselves to fight ovarian cancer. Yes, Early detection is crucial and it can help in prompt treatment proving better outcomes and enhancing quality of life for those affected.
